Managing cat arthritis is crucial in order to improve the lives of cats that suffer from this affliction. Arthritis is a disease most frequently seen in senior cats, but it can actually be present in any age cat. The information that could be useful for every cat owner includes the common causes, typical signs, methods of identification, and available treatments for cat arthritis. Here, you will find a review of several aspects of managing cat arthritis with helpful suggestions to improve your cat’s situation.
Understanding Cat Arthritis
What is Cat Arthritis?
Feline arthritis is an ongoing disease that affects the joints of the cats and causes discomforts like pains and joint rigidity. It is a health complication developed when cartilage that acts as shock absorber to the joints wears out and bones start touching one another. This can cause qualm and reduced life quality of cats that affected by this disease.
The Most Frequent Causes of Cat Arthritis
Several factors can contribute to the development of arthritis in cats, including:
Age: Arthritis is a common problem with cats, which may be attributed to the fact that senior cats are just long in the tooth and their joints are subjected to a lot of stress even if it is passive.
Genetics: Maine Coons and Persians and some other breeds are specifically known to be prone to arthritis due to genetic factors.
Obesity: Obesity also exert pressure to the joint thereby contributing to arthritis.
Joint Injuries: Arthritis can be caused by past injuries including fractures and dislocations of the affected joint.
Congenital Conditions: There are certain health problems that increase the cats’ vulnerability for arthritis, for example hip dysplasia.
Inflammatory Joint Diseases: Some diseases like rheumatoid arthritis may lead to inflammation as well as destruction of the joints.
Symptoms of Cat Arthritis

Early signs of cat arthritis should be identified so that it can be treated better in its early stages. Common symptoms include:
Limping or Lameness: Cats might limp on one leg compared to the other due to a discomfort that is associated with their joint pain.
Stiffness: Especially when there is break, or no much physical activity is involved.
Decreased Activity: Jugding from their decreased activity, cats may be less willing to jump, run or play.
Difficulty Climbing Stairs: Cats suffering forms of arthritis may find it difficult to climb stairs or try to access higher grounds.
Reduced Grooming: Arthritis also affects the cat’s ability to groom him or herself as the stiff joints will often prevent the feline from reaching all parts of the body such as the groin and belly.
Behavioral Changes: Overexcitement, anger, or avoidance are a signal of discomfort.
Weight Loss: Inactivity and some pain may cause a person to lose weight.
Swelling: Affected joints may become reddened, hot to the touch.
Diagnosing Cat Arthritis
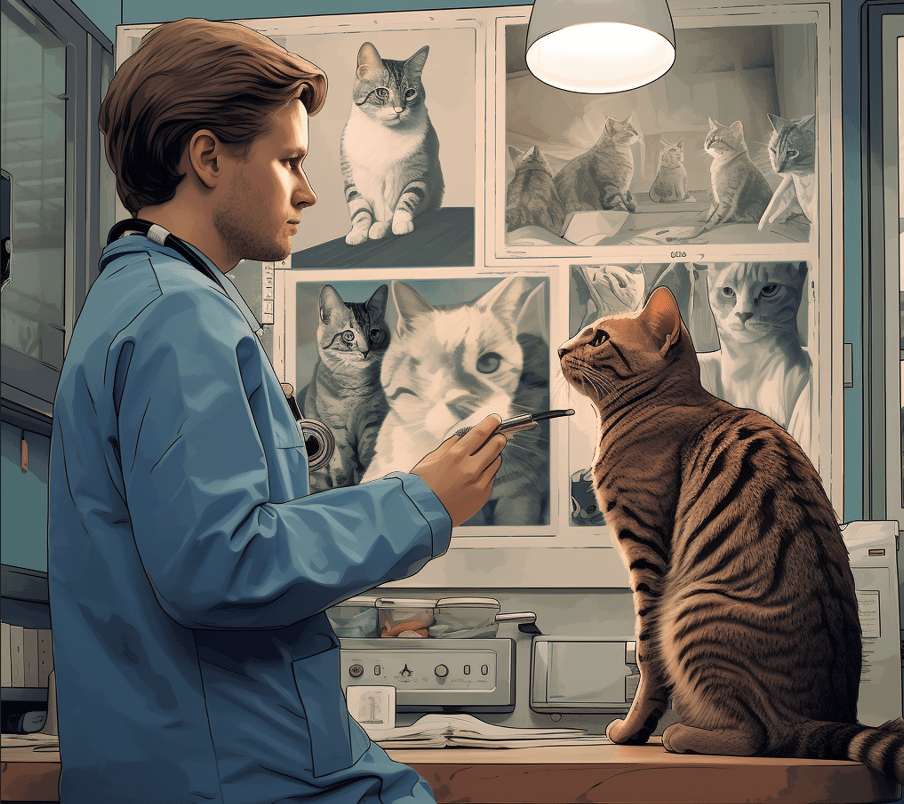
Veterinary Examination
In case you notice signs of arthritis in your cat it is important to have the cat checked by a veterinary at once. During a consultation with the vet, he or she will conduct a physical assessment to see if your cat has tick or fleas, or if your cat has any disease that makes it vulnerable to the parasite.
Diagnostic Tests
There are various test that can be done in order to confirm arthritis and the extent of the condition as well. These tests may include:
X-Rays: There are certain findings in radiology like X–ray that can show changes in the structure of the joint like spurs of the bone and lack of cartilage.
Blood Tests: In fact, blood tests can clear other diseases that have similar symptoms with those of fibromyalgia.
Joint Fluid Analysis: Pentration through the joints and conducting a analysis of the fluid will determine if it is inflamed or infected.
CT Scans and MRIs: Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography may help obtain the clear pictures of the joint and soft tissues.
Treatment Options for Cat Arthritis

Medications:Some medicines ease the pain and inflammation in cat arthritis, hired mate adjudged suitable for the cat. Choices embrace Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), analgesics or pain relievers, corticosteroids, and Disease-Modifying Osteoarthritis Drugs (DMOADs).
Dietary Management: Diet control exercise is important. Try to keep at a healthy weight, offer supplements for the joints such as glucosamine or chondroitin, increase the use of omega-3 fatty acids in the diet, and stay hydrated.
Physical therapy techniques: By sweetening water through exercising, massages, water exercises, and laser treatment, mobility can be enhanced, and the pain associated with the same reduced significantly.
Environmental modifications: Comfort and mobility are botulism improved by the environmental changes including the availability of soft beds, ramps and steps, easily accessible litter boxes, and easily accessible elevated food and water bowls.
Alternative therapies: Other complementary approaches such as acupuncture, chiropractic, herbal medicine/ supplements like curry spice/turmeric, and boswellia may also be of value.
Preventing Cat Arthritis
While arthritis cannot always be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk and promote joint health:
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Eliminate obesity by ensuring that the citizens have the right diet and they are active.
Provide Joint Supplements: Some added sources recommended to cat’s diets include joint supplements for support of joints.
Avoid Joint Injuries: Minimize your chances of developing arthritis by avoiding activities that might result in injuries that matter.
Regular Veterinary Check-Ups: Schedule your filial visits and those of your pet with your veterinarian in an effort to diagnose arthritis if it is still in its preliminary stage.
Recognizing Complications
We know that arthritis can be a complication if it is not handled well. Be aware of the following potential issues:
Decreased Mobility: Arthritis will limit your cat’s mobility and the ability to engage in activities that are quite common in their day to day lives.
Chronic Pain: If left untreated, arthritis may manifest its symptoms by causing the patient persistently experiencing pain and discomfort regularly.
Muscle Atrophy: Lastly, we know that sedentary activity can create adverse effects such as loss of muscle mass and muscle strength.
Behavioral Changes: Therefore, chronic pain alters the behavior of patient for example may become aggressive or withdraw from society.
Managing Cat Arthritis at Home
In addition to veterinary care, there are several steps you can take at home to manage your cat’s arthritis:
Monitor Your Cat’s Weight: Slim your cat in order to prevent undue stress on the joints.
Provide Gentle Exercise: Freely motivate low impact exercises to keep the feline lively.
Use Supportive Bedding: Choose comfortable comfortable and soft materials for the cots to lessen pressure to the joints.
Create a Comfortable Environment: There are alterations that one should make on cats environment in order to enhance their comfort and movements.
Administer Medications as Prescribed: Both the medication and the dietary supplements: There is often a certain way in which your vet will recommend you to give it to the dog and the rate in which to administer it.
Emotional Support for Cat Arthrities
Cats with arthritis require emotional support Because arthritis involves an underlying medical condition that is progressive most cats will be affected for the rest of their lives.

Arthritis is always a difficult problem both for owners of cats and the pets themselves. Providing emotional support is essential for your cat’s well-being:
Spend Quality Time Together: Cats require attention every once in awhile, and make sure to hug, cuddle or pet them to calm them down.
Gentle Grooming: Assistance with bathing for your cat if he has problems grooming certain parts of his body.
Provide Mental Stimulation: Provide your cat with toys and activity like toys, puzzles etc so as to enhance the mental ability of the cat.
Create a Calm Environment: Reduce stress in your cat by observing a low noise level around your cat.
When to Seek Veterinary Care
It’s important to seek veterinary care if your cat shows any of the following signs:
Severe Pain: In case your cat is experiencing any of the following symptoms: intense pain, labored breathing, persistent crying, see your veterinarian.
Significant Mobility Issues: If you have a scenario whereby your cat is unable to move or perform some minor tasks, take your cat to your vet.
Sudden Changes in Behavior: There are kids who when they are uncomfortable, they change behavior, for example, they become aggressive or withdraw.
Weight Loss or Reduced Appetite: Therefore, any change in weight or reduction in appetite without apparent cause, should be a cause for veterinary concern.
Long-Term Management and Care
It is important to note that, arthritis is a long-time illness that needs constant treatment. Regular veterinary check-ups and ongoing care are essential:
Regular Veterinary Check-Ups: Consult your veterinarian to make appointments for checkups to control your cat’s progression and modify its therapy when necessary.
Consistent Medication: Feed medications and supplements in a regular manner to your pet, if allowed by your vet.
Adjust Treatment Plans: Consult with your veterinarian when making changes to your cat’s therapy regimen according to his needs and reactions.
Monitor for Changes: It is also important that you monitor your cat’s condition and inform the veterinarian if your cat is in any new condition.
Conclusion

Feline arthritis requires a multimodal plan of treatment, which may comprise of medical treatment and on going treatments by the veterinarian, medications, feeding, exercising, and the state of environment. This paper reveals the signs, causes, and ways through which arthritis can be managed and treated hence helping the pet owner to find ways to enhance the life of his/her cat. I recommend daily or weekly checkups, if possible, plus any combination of exercise, medication, or behavioral modification to help an arthritic cat feel good and at ease. If you think your cat is affected with arthritis, you should consult your veterinarian so that the best strategies that would let your cat live a healthy and pain free life can be recommended.