Eye is the most important sensor of any animal. Like humans without active eye cats are mostly inactive. Their life becomes dependent on humans. They can’t do anything without help. So, for keeping a healthy and playful cat, you have to understand what type of issues can happen in a cat’s eye.
To watch the summary of this article, just watch this video-
Common Problems with Cats’ Eyes: What Every Pet Owner Should Know
As a cat owner, understanding the common problems with cats’ eyes is essential to ensuring their well-being. From minor issues like mild discharge to serious conditions such as glaucoma and cataracts, eye problems in cats can lead to discomfort and long-term health issues. Regular monitoring of your cat’s eye health can help catch problems early, preventing more serious conditions. Some common symptoms include squinting, excessive tearing, and cloudiness, which may indicate underlying issues. If you notice any of these signs, it is important to seek veterinary care to maintain optimal eye health for your feline friend.
How healthy eyes contribute to a cat’s well-being.
Cat’s Eye without any issues improves cats mental health and physical growth. Cats can easily navigate their environment and help them to understand how to get around. Healthy eyes help the cat to play with toys and practice hunting behaviors. Cats with eye conditions can feel uncomfortable. The high eye pressure may experience symptoms similar to headaches. This may happen for high glaucoma.
Cats with good vision ensure a healthy life and make them active.
Preventing Common Problems with Cats’ Eyes Through Regular Care
Preventing problems with cats’ eyes starts with regular care and preventive measures. Ensuring your cat is up-to-date on vaccinations can reduce the risk of viral infections that cause eye inflammation. Regular veterinary checkups are also crucial for detecting early signs of eye conditions like glaucoma, corneal ulcers, or cataracts. Additionally, keeping your cat’s living environment clean and free of allergens and irritants can help reduce eye irritation. Routine eye cleaning and ensuring that their diet supports overall health are vital for maintaining eye function.

Recognizing Problems with Cats’ Eyes: Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
Recognizing the early signs of problems with cats’ eyes can be challenging, as cats often don’t exhibit overt signs of pain. However, there are certain symptoms you should never ignore. If your cat begins squinting, having difficulty navigating, or exhibiting unusual aggression, these could all be signs of eye discomfort. Other symptoms like cloudy vision, excessive tear production, and swelling should prompt an immediate veterinary consultation. By paying close attention to behavioral and physical changes, you can help your cat avoid long-term vision issues or blindness.
Ocular cloudiness:
If you found your cat has ocular cloudiness, redness, or swelling. It is a symptom of eye problems.
Discharge:
if you find your cat has any type of fluid on eye-sight. It may be the symptom of eye problems.
Squinting:
Squint is when eyes do not align properly but look in another direction. It is also known as strabismus.
Reluctance to move around: if your cat can not move its eye, it is a serious problem. This is known as Oculomotor Dysfunction. In this case, the cat can’t control voluntary and purposeful eye movement. It hampers the cat’s daily work.
Bumping into objects:
bumping into objects could be a symptom of serious eye conditions. It could be a sign of eye conditions, including vertical heterophoria (VH), visual field defect, glaucoma, etc. There are other possible causes of bumping into things including not getting enough sleep, health issues that affect joints and muscles, such as arthritis, and Medications such as anti-anxiety, antidepressants, and anticonvulsant drugs.
Behavioral changes like anxiety or aggression:
behavioral changes are a major sign of defective eyes. Cats are like children; they can’t talk. For this reason, they change their as-usual behavior. They do this from anxiety which is created from visual problems.
Sign of infection on eye-sight: signs of infection are thick, yellow, green, or white discharge, often accompanied by other symptoms.
Understanding the Link Between Behavioral Changes and Problems with Cats’ Eyes
Eye health is closely tied to your cat’s overall well-being, and problems with cats’ eyes can manifest in various behavioral changes. Cats rely heavily on their sense of vision, and when they experience eye discomfort or vision impairment, it can lead to increased anxiety, irritability, or aggression. This is particularly common in conditions like glaucoma or ocular ulcers, which can cause pain and disorientation. Recognizing these behavioral shifts and seeking prompt veterinary care can help address the root cause and prevent further distress for your pet.
Anatomy of cat’s eye:
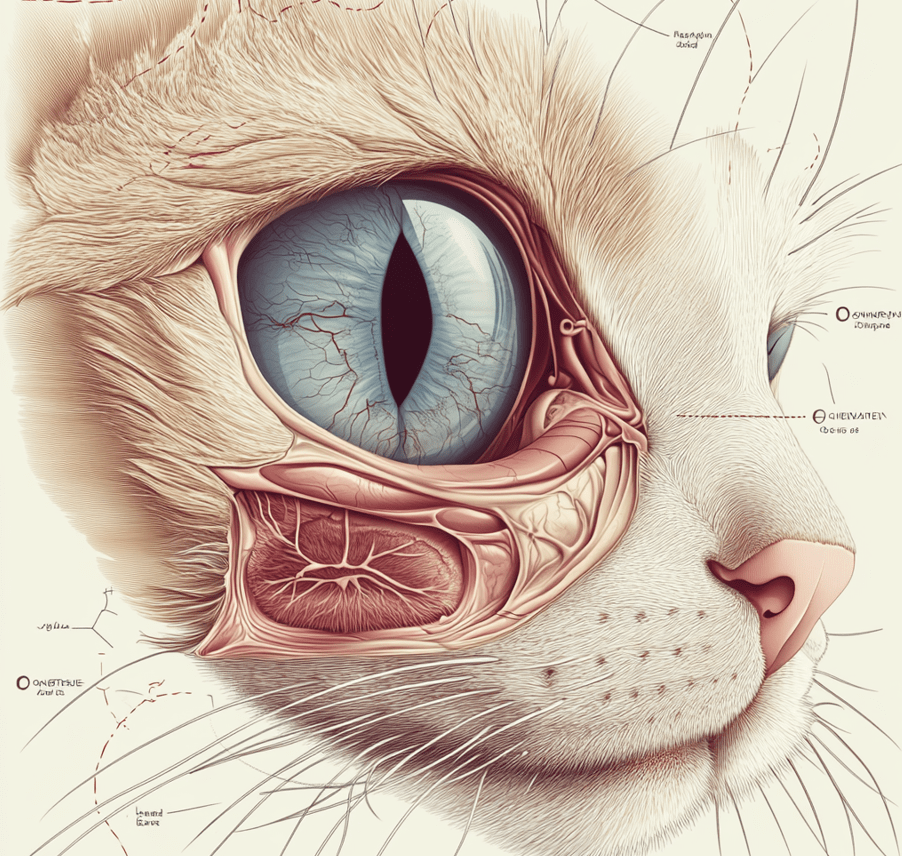
The structure of the Cat’s eyes is similar to that of other animals and similar to a large extent to humans.
The cat’s eyes consist of the bony cavity socket which is known as orbit, sclera, conjunctiva, cornea, pupil lens, cone cells, retina, rod cells, area centralis, optic nerve, nictitating membrane, lacrimal glands, meibomian glands, and so on.
Orbit is a structure formed by several bones, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and the structures that produce and discharge tears.
The sclera is the white section of the eye. It is the outer layer of the eye and covered by a thin membrane which is known as conjunctiva, located near the front of the eye. Conjunctiva covers the inside of the eyelid.
The cornea is a crystal clear dome on the front surface of the eye. It helps light enter into the eyeball and helps to focus the light on the retina. The retina contains the cells that sense the light. There are two types of cells which absorb light and produce signals to generate images in the brain. The most sensitive area of the retina is called area centralis which contains thousands of photoreceptor cells.
Cat’s eyes are the only sensor of its body that deals with light and gives visual opportunity. So you have to take your cat to their regular veterinary visits. It is the key part of maintaining their eye health. A vet is an expert for your cat’s eye health to check any dysfunctional issue.
Common eye health issues in cats:
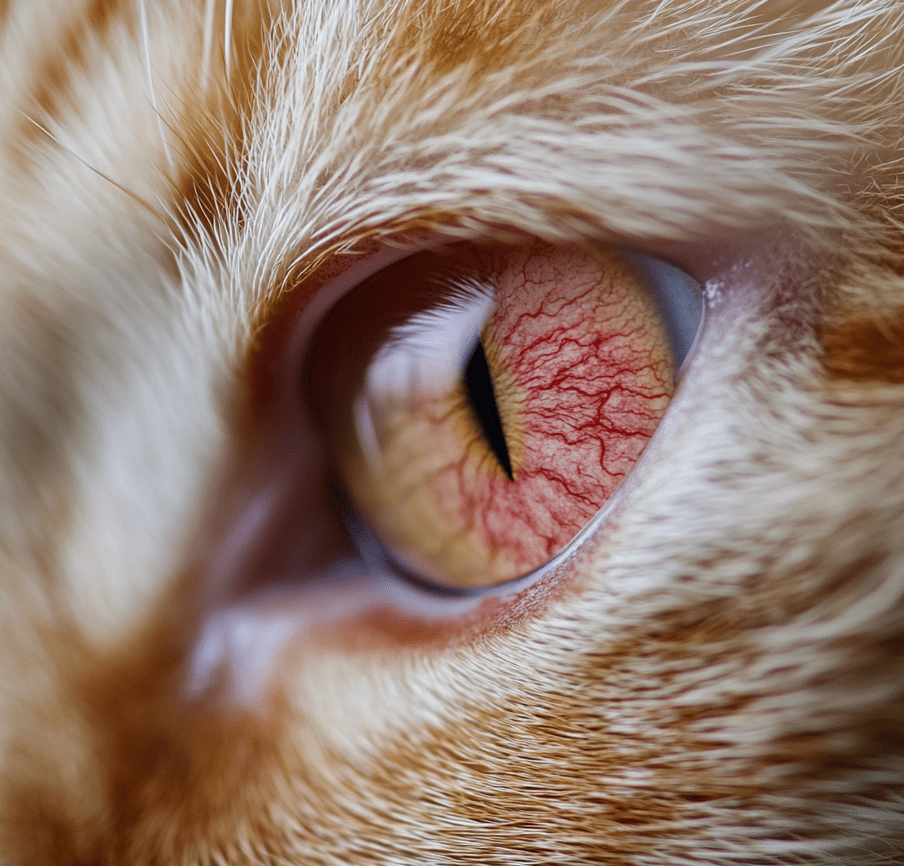
Conjunctivitis:
It is also known as pink eye. It is a condition in cats that causes inflammation of the conjunctiva which is the mucous membrane that lines the eyelids and covers the eyeball.
Symptoms: if you find your cat has redness, swelling, pain, discharge, watery eyes, and a third eyelid that’s more visible, it may be Conjunctivitis.
It happens due to the reaction of viruses, bacteria, allergens, dust, foreign objects, trauma, and other factors. There are other causes such as Eye ulcers, parasites, immune-mediated diseases, systemic diseases, allergies and environmental irritation, glaucoma, uveitis, tear duct diseases, eyelid and eyelash problems, and eye tumors.
Treatment: Provide anti-inflammatory drugs to your sick cats, use lubricating eye drops, antibiotic eye drops, and antiviral medications.
Corneal ulcers:
it is painful sores on the surface of a cat’s eye. It happens due to trauma, disease, or other factors. Corneal ulcers happen due to scratches from other animals, thorns, or playing with sharp objects. Corneal ulcers can not be seen with the open eye. So, a vet is needed for better treatment. If you don’t treat, corneal ulcers may turn into blindness or even loss of the eye.
Cataracts:
It is a condition of the eye where the lens of the cat’s eye becomes cloudy or opaque which interferes with their vision. Cataracts can happen due to several things like uveitis which is the inflammation within the eye, genetic, trauma or injury to the eyesight, diseases like high blood pressure or diabetes, nutritional imbalances, radiation exposure, cancer, and viral bacterial, fungal or protozoan eye infections.
Signs of cataracts:
Cloudy, hazy appearance in one or both eyes is the major symptom of cataracts. Bumping into furniture, difficulty finding food or litter box, white bluish-gray pupils, and hiding more than usual are other signs of cataracts.
Treatment: Surgery is the only treatment for cataracts. In the most common surgical procedure, ultrasound is used to break cataracts. After that, an artificial lens is implanted to restore the vision of cats.
Glaucoma:
When the eye’s drainage system fails, then glaucoma occurs due to the buildup of high fluid pressure inside the eye. Primary and secondary, mainly these two types of glaucoma observed in cat’s eye. Secondary glaucoma is more common than primary glaucoma and can affect both eyes. Primary glaucoma is very rare to find.
Treatment: The treatment of glaucoma is a long-term treatment. Instant treatment can prevent blindness, but treatment must be carried on to fully cure it. Eye drops, Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, and beta blockers can be used for glaucoma treatment.
Treatment Options for Problems with Cats’ Eyes: What to Expect
Treatment for problems with cats’ eyes depends on the underlying condition and severity of the issue. For conditions like conjunctivitis or mild corneal ulcers, medications such as antibiotic or anti-inflammatory eye drops may be prescribed. In more severe cases, such as cataracts or glaucoma, surgical intervention may be required. Glaucoma treatments often involve long-term eye drops to reduce fluid buildup, while cataract surgeries aim to restore vision with an artificial lens. Early detection and treatment are key to ensuring the best possible outcome for your cat’s eye health.
Tear duct blockage or over-production:
The nasolacrimal duct of a cat drains tears from the eye to the nose. Sometimes it can become blocked due to inflammation, tumors, or other causes. Uveitis, corneal problems, conjunctivitis, abnormal growth of eyelashes, etc. can cause duct blockage. Overproduction of tears can happen due to allergies, infections, or eye injuries. In maximum cases, it is not a serious issue or medical concern.
When seeking emergency care:

If your cat faces sudden blindness, there is no option to delay. You have to take your cat to emergency care. Sudden blindness may come from various issues like high blood pressure, retinal detachment, uveitis, brain disease, retinal degeneration, head trauma, taurine deficiency, medication overdose, etc.
Rapid swelling or severe redness indicates a serious condition. So, do not delay. And consult a vet immediately. Otherwise, your cat can become blind.
For maintain a healthy life of your cat, there is no alternative without regular checkups with a vet.