Understanding cat Urinary Tract Infection will help cat owners to keep their cats happy and free from diseases that could have caused the ailment. UTIs can be painful and may result in other complicated health complications if not treated. This article is a good starting point for cat owners to know about the cat urinary tract infection causes, signs, diagnosis, management and prevention.
To watch the summary of this article, just watch this video-
What are Cat Urinary Tract Infections?
Feline lower urinary tract diseases are inflammatory conditions secondary to bacterial pathogens that infest the urinary system in cats, involving the bladder and the urethral preload. UTIs are formed when bacteria penetrate the urinary system, increase their quantity and produce irritation of the urinary tract. Although rarer in cats than in dogs, the condition may develop and if not treated in time it may result in severe complications.
Types of Urinary Tract Issues in Cats
It’s important to distinguish between different types of urinary tract issues that cats can experience:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Bacterial infections of the urinary system and bladder which cause inflammation and pain.
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD): A group of diseases in the lower urinary tracts; infections, bladder stone formation, and obstruction of the urethra.
Bladder Stones: Ionic material precipitates that develop in the bladder and can lead to pain and problems urinating.
Urethral Obstruction: This is normally the inability to urinate freely due to blockage along the urethra tract by formation of stone usually along the bladder.
Causes of Cat Urinary Tract Infections

Several factors can contribute to the development of urinary tract infections in cats, including:
Bacterial Infections: Thus, bacteria like E. coli are the most frequent pathogens of infections among cats, which spreads through the urethra into the urinary system.
Underlying Health Conditions: Diabetic, kidney diseased and hyperthyroid cats are common individuals for developing UTIs.
Dehydration: Frequent and clear examples include inadequate liquid consumption leading to formation of thick urine; this promotes bacterial production.
Urinary Tract Abnormalities: Congenital anomalies and abnormalities of the urinary tracts put cats under different risks of infections.
Bladder Stones: Bladder stones may act as a source of irritation to the bladder wall and thereby cause a predisposition to bacterial infection.
Stress: Urinary problems may occur in situational changes like the addition of other pets in the family or transfer to another home.
Symptoms of Cat Urinary Tract Infections
The common signs of cat urinary tract infections must be detected early in order to prevent their progression to a severe stage. Common symptoms include:
Frequent Urination: Pets with UTIs may try to urinate more often, and in smaller amounts.
Straining to Urinate: Painful or trying to urinate could be due to a UTI or another urinary tract infection.
Blood in Urine: A usual symptom of a UTI is hematuria which is the appearance of blood in the urine.
Painful Urination: Some cats with UTIs may show symptoms of pain when they pass urine, they may his or meow while urinating.
Licking the Genital Area: This is because licking of the genital area can be as a result of discomfort or irritation that is more when it is excessive.
Urinating Outside the Litter Box: Under the UTI, the cat may move around the house to use a particular area to urinate because of pains or have the urge.
Behavioral Changes: The following are examples of signs of a UTI; changes in behavior may indicate a UTI – becomes easily irritated or start hiding.
Making Diagnosis of Cat Urinary Tract Infections
Veterinary Examination
If you think your cat has a UTI, then the best thing to do is to bring your cat to your vet so you can get a check up. Your cat’s medical records will be examined, and the vet will proceed to check the animal for any sign of pain or unusuality.
Urinalysis
Urine samples are among the most important tools for diagnosing UTIs. Vet will use a special technique to obtain urine sample and determine its composition and concentration as well as analyse for the presence of haemoglobin, leucocytes, nitrites, specific gravity and crystals.
Urine Culture
A urine culture involves culturing of the bacteria from the urine sample taking to the laboratory in order to identify the type of bacteria that has cause the infection. This aids the vet in choosing the right antibiotic to give to the patient.
Imaging
Lastly, certain body structure tests for instance ultrasound or X-rays can help in establishing the status of the urinary system. Such investigations can show a distortions that exists, for example, the presence of stones or malignancy in the urinary bladder which contributes to the infection.
Treatment of Cat Urinary Tract Infections

Antibiotic Therapy
The main treatment for bacterial urinary tract infections is through the use of antibiotics. They will be given antibiotics depending on the bacteria indicated by the urine culture test. This mandates it is important to use antibiotics as directed by your doctor till the last drop even if the symptoms improve halfway through the course.
Pain Management
This is especially important for cats with this disease since UTI can be painful. Your vet may also recommend that you give your pet pain killers or anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and inflammation.
Fluid Therapy
It may be required to perform some form of intravenous therapy to facilitate the cleansing of urinary system organs and to complement kidney capability. This might entail supplying the client with substances intradermally that is, under the skin or intravenously that is, into the bloodstream.
Dietary Changes
There are smooth varieties of food that one needs to undertake to avoid or overcome the problems associated with urinary tract problems. The vet may prescribe specific food specifically for your pet’s urinary health and to avoid the formation of bladder stones.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
It is crucial to get your pet checked up frequently especially by the vet after the treatment and sometime after the infection has been treated occasionally. The vet may sometimes advise that your cats should undergo urinalysis and or urine cultures in order to check on the cat’s urinary conditions.
Prevention Tactics for Cat Urinary Tract Infections
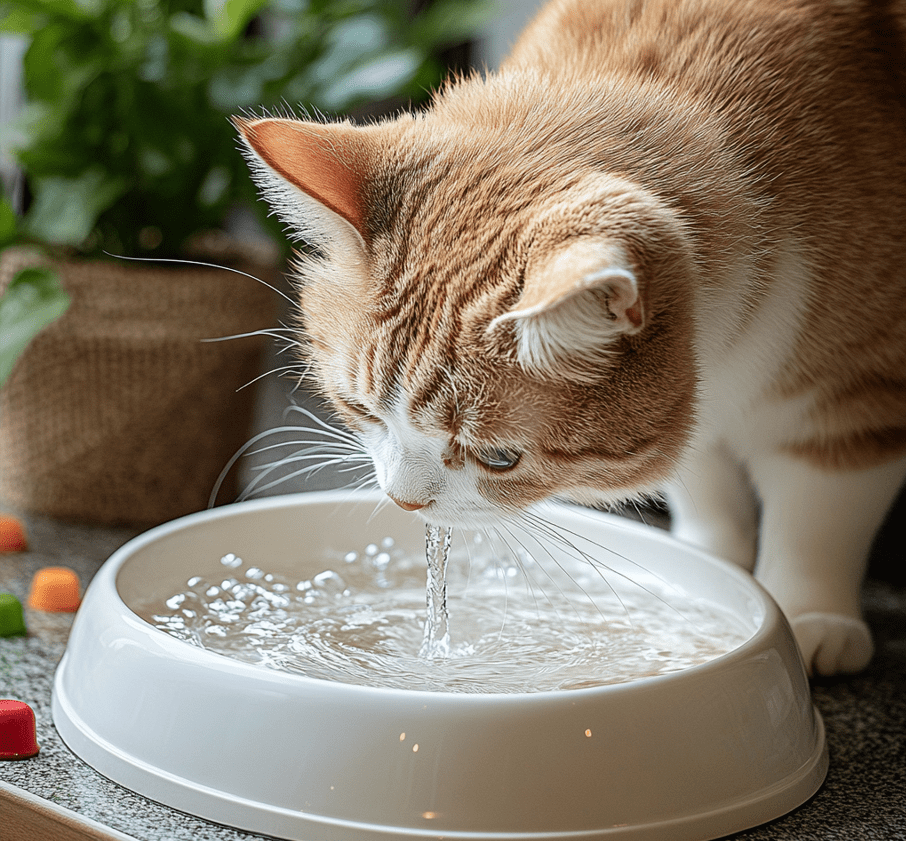

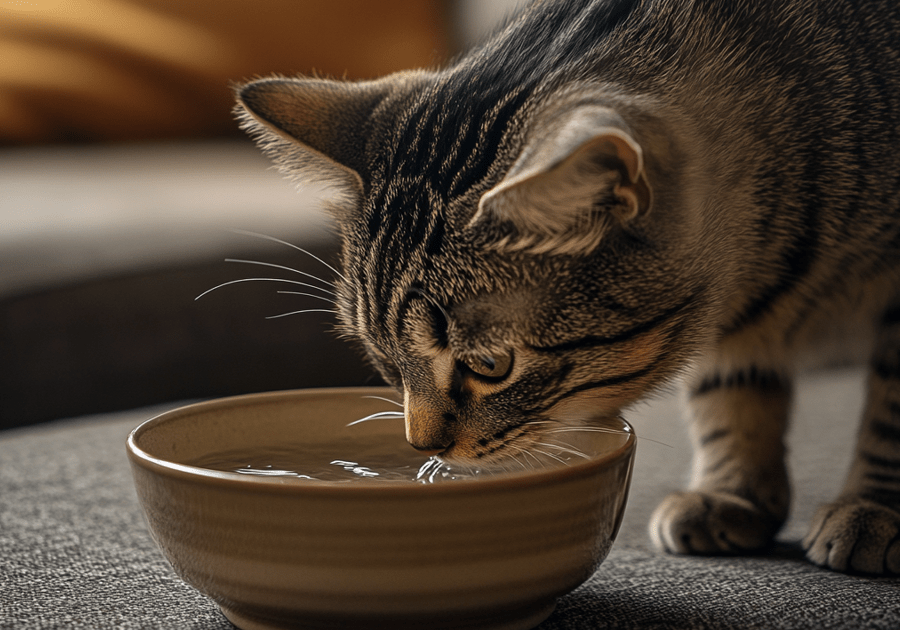
Hydration
Keeping your cat’s water intake high should be a priority in order to avoid developing a urinary health problem. Have a constant supply of fresh water, and if you can add a water fountain in the enclosure of your cat it will greatly encourage it to drink. In the same respect, wet food can also boost the amount of fluids your cat takes into his body.
Proper Litter Box Maintenance
For the urinary system to be healthy, the litter box should always be clean. Regularly, clean the litter box and also change used litter periodically in order to prevent bacterial formation. The litter box should be placed in a low-traffic area and, if you have more than one cat, you should provide several litter boxes.
Stress Reduction
Stress is known to cause UTIs and that means minimizing stress can go a long way in preventing UTIs in cats. Establish a daily schedule and attempt not to rearrange the existing schedule drastically, and give your cat toys and surfaces to play with that help to develop its mind.
Regular Veterinary Check-Ups
Periodic vet visits help in discouraging any attainable health complications and could examine for the initial symptoms of the issue in your cat’s urinary system. Annual or biannual wellness.